RELX
1.0000


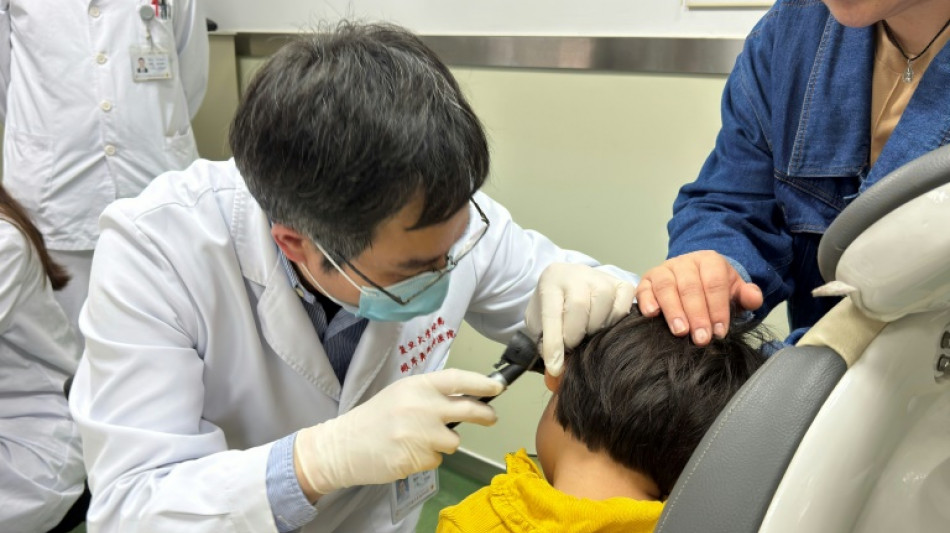
Zhu Yangyang babbles away like a typical happy three-year-old, calling out for "mama" and "papa" and accurately naming colors -- a remarkable achievement considering he was completely deaf just months ago.
He is one of five children whose hearing was restored through a revolutionary new gene therapy in a clinical trial led by Chinese and American researchers, offering new hope for those born with a rare genetic mutation.
Yangyang's mother Chang Yiyi says she was moved to tears when she realized, around three weeks after the treatment last September, that Yangyang could hear her knocking on the door.
"I hid in a closet and called for him, and he still responded!" she told AFP in an interview from Shanghai.
The results of the study, published Wednesday in the prestigious journal Nature Medicine, mark the first time the procedure was performed on both ears. This led to significant improvements in speech perception and the ability to locate the source of sounds compared to treatment in just one ear.
"This is absolutely a turning point," Zheng-Yi Chen, the study's senior author at the Eaton-Peabody Laboratories at Mass Eye and Ear, told AFP, adding companies are now conducting clinical trials, including two in Boston, with the goal of moving towards regulatory approval.
"If the results hold, without any complications, I think in three to five years, it may be a medically approved product," he added.
- Rare mutation -
There are around 26 million people globally with genetic forms of deafness, with this particular therapy focusing on people born with a mutation of the OTOF gene -- roughly two to eight percent of inherited deafness cases.
This defect means they are unable to produce the protein otoferlin, which is needed for hair cells in the inner ear to convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that can be sent to the brain.
The treatment involves injecting a modified virus into the inner ear that smuggles in a working version of the OTOF gene, restoring hearing.
When they realized that Yangyang could hear for the first time, "the whole family cried" including Yangyang's mother and grandmother, said lead study author Yilai Shu of the Eye & ENT Hospital of Fudan University in Shanghai.
Chang, a 26-year-old homemaker, said that taking care of her son has become much easier since he began developing language skills, and the family soon hopes to move him from a speech rehabilitation school to traditional kindergarten.
- More genetic targets -
Shu led the research team that delivered the very first OTOF gene therapy in 2022, pioneering a treatment that has since been administered to more children around the world, including in the United States and the United Kingdom.
Treating both ears presented new challenges, he told AFP. Doubling the surgical procedures increased the risk of side effects.
However, careful dosing minimized the immune response, and only mild to moderate side effects -- like fever, vomiting and slightly elevated white cell counts -- were observed.
All five children, who ranged in age from one to 11, saw major improvements.
Two of them gained an ability to appreciate music -- a more complex acoustic signal -- and danced happily in videos recorded for the study.
Surprisingly, even the 11-year-old has gained some capacity to understand speech and talk, even though it was expected it would be too late for the brain to acquire this ability if it had never before perceived sound.
"That really shows our brain has a plasticity that maybe lasts much longer than we originally thought," said Chen. The clinical trial is ongoing, and the participants will be monitored for long-term follow up.
Meanwhile, Shu and Chen said they are working on further animal testing to develop treatments for other causes of genetic deafness, including those related to the GJB2 gene -- the most common cause of deafness present at birth.
V.Fan--ThChM